How to Reboot Routers for Better Performance and Stability
If you’re experiencing slow internet speeds, dropped connections, or other network issues, knowing how to reboot routers can be a quick solution. Rebooting clears temporary data, resets connections, and can resolve minor problems that affect your network’s performance. In this guide, we’ll explore the different methods to reboot routers effectively, including tips to resolve common connection issues and when to consider upgrading your equipment.
Reasons to Reboot Your Router
You may want to reboot your router for several common reasons, including:
- Connection Problems: Experiencing dropped or lagging connections? A reboot can refresh the network connection, potentially restoring stability and speed.
- Firmware Issues: Routers sometimes receive firmware updates that require a reboot to apply changes effectively, which can improve security and performance.
- Overheating: Routers, like other electronics, can overheat after prolonged use, affecting their functionality. A reboot gives the device a brief pause to cool down.
- Network Security: Restarting your router regularly can clear out temporary data and add a layer of security, helping to protect your network from minor vulnerabilities.
Methods to Reboot Routers
There are several methods to reboot routers, depending on the type of router and your network setup. Here’s how to do it:
Hard Reset by Disconnecting Power
- A hard reset is a straightforward way to reboot your router. Simply unplug the router from the power source and wait at least 10 seconds before plugging it back in. This clears any temporary data and allows the router to reconnect to the network with a fresh start.
- Tip: Avoid just pressing the power button if your router has one; unplugging ensures a complete power cycle.
Access the Router’s Configuration Page
- Many routers offer the option to reboot through their configuration page, which you can access via a web browser.
Step-by-Step:- Open your web browser and type 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 into the address bar (this varies by router).
- Log in using the default username and password, often admin/admin or as indicated on a label on the back of your router.
- Navigate to the settings or administration section and look for a “Reboot” or “Restart” option.
- Open your web browser and type 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 into the address bar (this varies by router).
- Tip: If you don't know how to access the router's configuration page, check your router from underneath and look for the stickiest part. Usually, the manufacturer will include instructions on how to access the router's configuration page, as well as a login and password. If your router does not have such a sticker, contact your ISP to obtain your login details.
Remove the Battery (If Applicable)
- For routers with an internal battery, like some portable models, another reboot method is to remove the battery temporarily.
- Steps:
- Power off the router, remove the battery, wait about 10 seconds, then reinsert it.
- Turn the router back on to complete the reboot process.
Reset to Factory Settings
- If you continue experiencing issues after a reboot, a factory reset can help. This option restores the router to its original settings and erases custom configurations, which can fix persistent issues.
- Methods:
- Through the configuration page: Look for a “Restore to Factory Defaults” or similar option.
- Using the reset button: Locate the small reset button (often recessed) on the back of the router. Press and hold it for about 10-15 seconds until the router restarts.
- Through the configuration page: Look for a “Restore to Factory Defaults” or similar option.
Inspect the RJ45 Cable for Damage
- If you use an Ethernet connection, inspect the RJ45 cable connecting your router and device. Damaged or improperly connected cables can cause issues with internet connectivity.
- Tip: Replace bent, frayed, or damaged cables with new ones to ensure a stable connection.
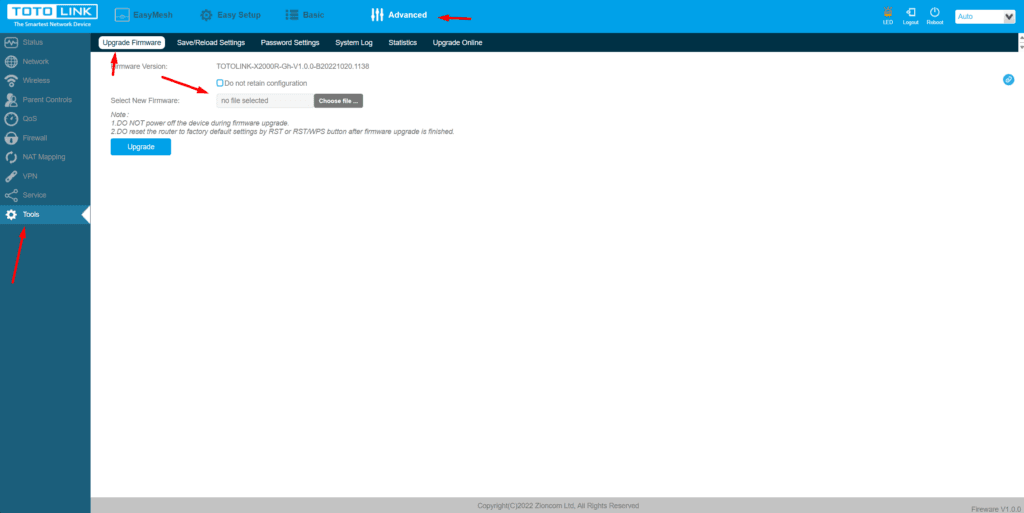
Update Router Firmware
- Firmware updates can resolve known issues, enhance security, and improve performance. Updating firmware is typically done through the configuration page.
- Steps:
- Access the router’s configuration page.
- Go to the firmware update section, often under “Maintenance” or “Advanced Settings.”
- Follow the prompts to check for updates and install the latest version if available.
- Access the router’s configuration page.
Contact Your ISP or Consider a New Router
- If none of the above methods work, contact your ISP for assistance. They can help determine if the issue is with your router or the network itself. If your router is older, consider upgrading to a newer model, as outdated equipment may no longer perform optimally on modern networks.
Additional Resources for Router Rebooting
For more in-depth guides on troubleshooting internet connectivity, check out these helpful resources:
Conclusion
Learning how to reboot routers can resolve minor connectivity issues and keep your internet connection running smoothly. From a simple power reset to a complete factory reset, these methods provide flexibility to address different issues. Remember to keep your router firmware updated and inspect cables regularly. If problems persist, consult your ISP or consider upgrading to a newer router for the best performance.
By following these steps, you can maintain a stable, secure, and fast internet connection for all your devices.