How to Disable Windows Indexing – What Is Windows Indexing?
Windows indexing is a built-in feature in the Windows operating system designed to enhance file searches. When you search for files, documents, images, or other data on your computer, Windows indexing speeds up this process by creating a catalog of the contents and properties of files. Essentially, indexing helps Windows keep a record of the files on your computer, making searches faster by avoiding the need to scan the entire disk each time.
Introduced in early versions of Windows, indexing has become an integral part of how Windows manages and retrieves data efficiently. However, while it can be beneficial for frequent file searches, there are times when users might prefer to disable Windows indexing to improve overall system performance, especially if they have fast SSDs or do not rely on the Windows search function heavily.
History of Windows Indexing in Windows
Windows indexing was introduced in Windows 2000 and has been part of every version of Windows since then. It was designed as a response to growing user demand for faster file searches, especially as hard drives grew larger and more users stored thousands of files on their computers.
With each version, Microsoft has improved Windows indexing, adding new capabilities to streamline file access and reducing the load it places on system resources. In modern versions like Windows 10 and Windows 11, indexing has become even more efficient, but it still has some downsides, particularly for users with slower systems or those who prioritize raw processing power over search speed.
Advantages of Windows Indexing
While some users may choose to disable Windows indexing, it does offer several advantages:
- Faster File Searches: Indexing makes it possible to search files almost instantly. When you search for a specific document, image, or program, Windows can find it quickly because it only needs to search the index, not the entire disk.
- Improved Search Capabilities: Windows indexing can search inside files (like documents and PDFs) for keywords, which is useful for users who need to find specific information within files.
- Better Resource Allocation: Windows manages the indexing process in the background, attempting to use minimal resources, especially when the computer is idle.
For many users, these benefits justify keeping indexing enabled, especially if they regularly rely on the Windows search feature.
Drawbacks of Windows Indexing
Despite its advantages, Windows indexing has some notable downsides that lead some users to disable it:
- Increased Disk Usage: Windows indexing constantly scans your files, which can lead to high disk usage. This can be particularly noticeable on older or slower hard drives, where the indexing process may slow down the computer. (This can lead to faster SSD degradation!)
- Memory and CPU Usage: Although Windows tries to run indexing in the background, it can still consume CPU and RAM resources, especially when adding or removing many files.
- Reduced Battery Life: For laptop users, continuous indexing can drain the battery faster as the hard drive and CPU stay active to maintain the index
Given these drawbacks, many users decide to disable Windows indexing to reduce disk usage, preserve system resources, and extend battery life on laptops.
Why Disabling Windows Indexing Can Be Beneficial?
Disabling Windows indexing is a common practice among users who prefer to prioritize system performance over search speed. Without indexing, your computer won’t continually scan files in the background, leading to less strain on the CPU, RAM, and disk. Here are some key benefits of disabling Windows indexing:
- Improved System Speed: Disabling indexing can improve overall system responsiveness, particularly on older systems or computers with limited RAM and CPU power.
- Lower Disk Usage: Without indexing, the computer reduces disk activity, which is beneficial for systems with traditional HDDs that are sensitive to constant reads and writes.
- Better Battery Life: For laptops, disabling Windows indexing can result in better battery performance, as the hard drive and CPU won’t be engaged in continuous indexing tasks.
- Extend SSD life: Windows Indexing can negatively affect the lifespan of an SSD, for this reason it is recommended to turn of Windows Indexing feature.
Overall, disabling Windows indexing is beneficial if you rarely use the Windows search feature, especially if your system has an SSD or you prefer to use alternative search tools.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Disable Windows Indexing
If you’re ready to disable Windows indexing, follow these steps:
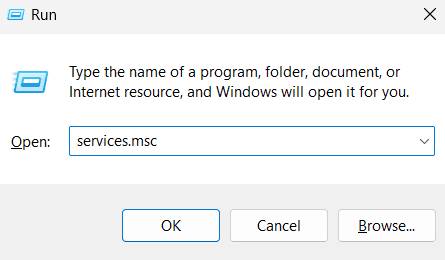
- Open the Services Panel
- Press Windows Key + R, type in services.msc, and press Enter. This opens the Services window, which controls various background processes.
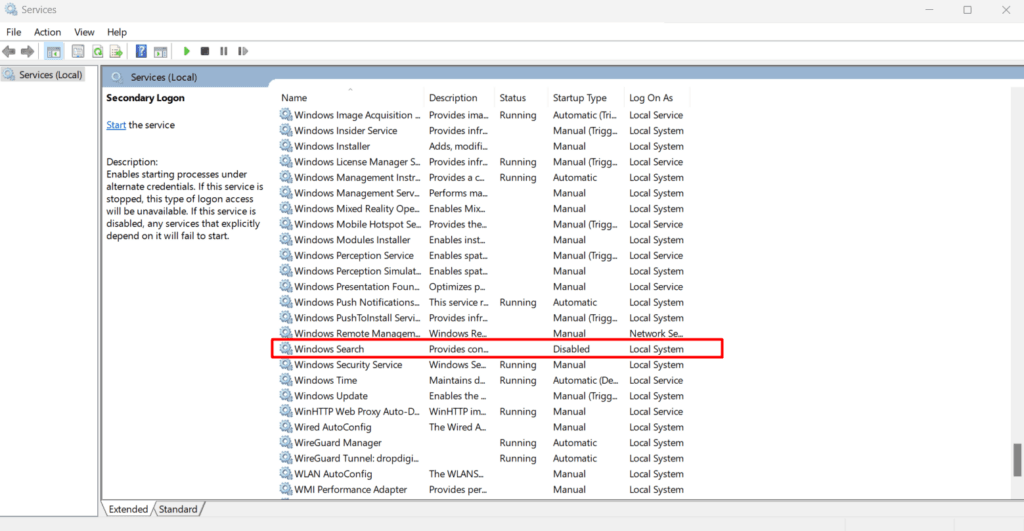
- Locate Windows Search
- In the list of services, scroll down to find Windows Search. This is the service responsible for Windows indexing.
- Disable Windows Search
- Right-click on Windows Search and select Properties.
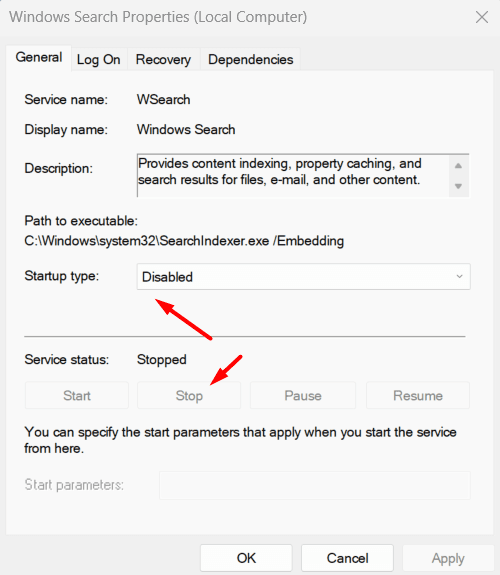
- In the Startup type dropdown, choose Disabled. This will prevent Windows from indexing in the future.
- Click Stop if the service is currently running, then click Apply and OK.
- Right-click on Windows Search and select Properties.
- Disable Indexing on Specific Drives (Optional)
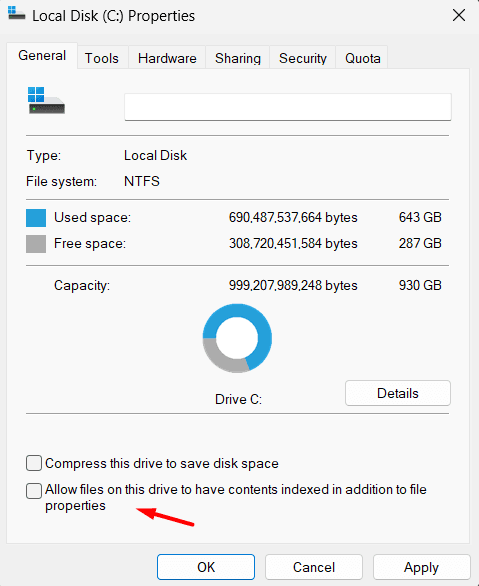
- If you want to disable indexing on specific drives only, open This PC or File Explorer.
- Right-click on the drive (e.g., C:), select Properties, and uncheck the box that says Allow files on this drive to have contents indexed.
- Click Apply, and choose whether to apply the changes to the drive and its subfolders.
- If you want to disable indexing on specific drives only, open This PC or File Explorer.
- Verify Indexing Is Disabled
- Go to the Windows search bar and type in something you know should be indexed. You’ll notice that search results may take longer, confirming that indexing has been disabled.
- Go to the Windows search bar and type in something you know should be indexed. You’ll notice that search results may take longer, confirming that indexing has been disabled.
This process will completely disable Windows indexing, improving system performance by reducing background activity.
Conclusion
Disabling Windows indexing can be a simple yet effective way to boost system performance, especially for users who don’t rely on Windows search regularly. While indexing offers clear benefits in terms of faster searches, its continuous background activity can drain resources and slow down some systems. By following these steps to disable Windows indexing, you can enjoy improved responsiveness, lower disk usage, and better battery life—especially if you use an alternative search tool.
External Resources: