Introduction
VPN (Virtual Private Network) services have exploded in popularity over the past few years, particularly due to relentless promotions by content creators on platforms like YouTube. Many influencers paint VPNs as an all-encompassing solution to internet security issues, suggesting they offer complete protection against hackers, ransomware, trojans, and more. However, this oversimplified portrayal misleads audiences and distorts the reality of what VPNs can actually do. While VPNs have certain valuable uses, they are by no means a “one-stop shop” for online security.
This article aims to clarify what VPNs can and cannot do, analyze why creators promote them so aggressively, and provide realistic tips for online safety beyond VPN use.
What VPNs Actually Do?
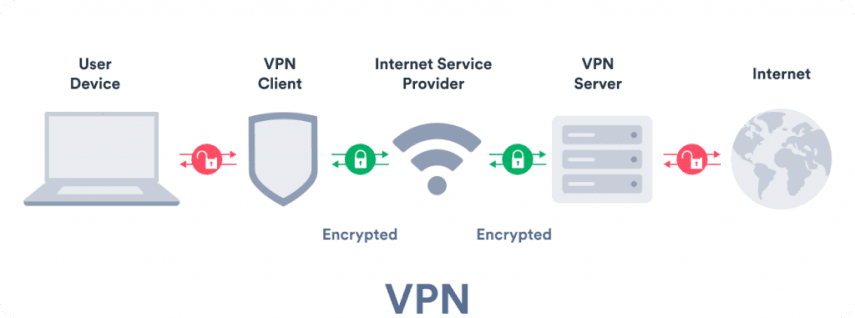
How VPN Services Work
VPNs create an encrypted connection, or “tunnel,” between a user’s device and a VPN server, masking the user’s IP address and encrypting their data while it’s in transit. This means that anyone intercepting the data (such as an ISP or a potential attacker) sees only encrypted information, keeping the user’s online activity private. The server’s IP address becomes the user’s virtual location, which can be useful for bypassing geographic content restrictions.
Why VPN Services Are so Widely Promoted on YouTube and Other Platforms
VPN companies offer generous affiliate commissions and sponsorship deals, making them an attractive source of revenue for content creators. Sponsorships are particularly lucrative for YouTube influencers who cater to audiences interested in tech, gaming, streaming, and privacy. Furthermore, the “fear factor” surrounding internet security makes VPNs an easy sell. By framing VPNs as essential tools for protecting against a variety of online threats, influencers can amplify their appeal and conversions, even if it means exaggerating or misrepresenting what these tools actually accomplish.
The Myths: What VPNs Don’t Do (Despite What Creators Might Say)
Despite the value VPNs offer, they are often marketed in ways that exaggerate their capabilities. Below are some common misconceptions that influencers frequently spread about VPNs.

Myth #1: VPNs Protect Against Ransomware
Reality: VPNs are not a tool for ransomware protection. Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a user’s files and demands payment to restore access. Ransomware typically infiltrates a system through malicious downloads, phishing emails, or exploitative software vulnerabilities. A VPN does not prevent these types of attacks, as it only encrypts data in transit rather than scanning or protecting against malware. To protect against ransomware, users should:
- Regularly back up important data.
- Avoid downloading suspicious attachments or clicking on unknown links.
- Keep software and operating systems up-to-date to minimize vulnerabilities.
Myth #2: VPNs Defend Against Trojans
Reality: A VPN cannot protect a device from trojans. Trojans are a type of malware disguised as legitimate software, often downloaded unknowingly by users. They give attackers access to the device once installed. Since trojans infiltrate at the device level, VPNs, which only affect data in transit, are ineffective against them. To prevent trojans, users should:
- Download software only from trusted sources.
- Use reputable antivirus software to detect and quarantine trojans.
- Avoid clicking on unknown links or downloading unexpected attachments.
Myth #3: VPNs Stop All Malware
Reality: VPNs cannot directly protect against malware. Malware refers to various malicious software, including viruses, spyware, adware, and more. VPNs do not have built-in malware protection features like antivirus programs do. They may prevent certain types of data logging or tracking, but they cannot identify, block, or remove malware from a device. To guard against malware:
- Use reliable antivirus software.
- Avoid downloading files from unknown websites.
- Regularly update software to patch known vulnerabilities.
Myth #4: VPNs Prevent Password Leaks
Reality: VPNs cannot stop password leaks if your credentials are compromised elsewhere. If an attacker gains access to your login information through phishing, social engineering, or data breaches on a platform, a VPN will not protect these credentials. To safeguard against password leaks, users should:
- Use unique, strong passwords for every account.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added security.
- Consider using a password manager to store and generate complex passwords securely.
What VPNs Can Actually Do: The Real Benefits
Hide Online Activity from Your ISP
VPNs can prevent ISPs from tracking your online activity by encrypting your internet traffic. This can be especially useful in regions where ISPs sell browsing data to advertisers or where users may face throttling based on certain online activities, like streaming or downloading.
Provide Secure, Encrypted Connections
One of the primary functions of a VPN is to secure data in transit by encrypting it. This is beneficial when using public Wi-Fi networks, where hackers may attempt to intercept personal information. A VPN adds an additional layer of security, helping users protect their data from prying eyes in such environments.
Access Geo-Restricted Content
VPNs are popular among users who want to access content only available in certain countries. For instance, users can change their virtual location to watch region-locked shows on Netflix or other streaming services. While this is not a security feature, it’s a convenient use case that draws many people to VPN services.
How to Stay Truly Safe Online?
Relying solely on a VPN for complete online security is a mistake. Here’s a realistic approach to staying safe online:
Be Cautious of Suspicious Links and Attachments
One of the most common ways malware spreads is through email attachments, social media links, and unknown websites. Avoid clicking on links from unknown sources, and be wary of attachments in unsolicited emails.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Wherever possible, enable 2FA to add an extra layer of security to your accounts. 2FA apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy are preferable to SMS-based authentication, as SMS can be intercepted through SIM-swapping attacks.
Use a Password Manager
A password manager generates and stores strong, unique passwords for every account, reducing the risk of reusing passwords across sites, which can lead to widespread account compromise if one password is exposed in a data breach.
Use Reliable Antivirus Software
Installing antivirus software, such as the built-in Windows Defender, is essential for scanning and blocking potential threats. For Android devices, avoid downloading apps from outside the Google Play Store, as these can often contain hidden malware.
Keep Your System Updated
Regularly updating your operating system and applications ensures that you are protected against the latest security vulnerabilities. Many ransomware and malware attacks exploit outdated software to infiltrate devices.
Conclusion
While VPNs offer some valuable privacy benefits, they are not the ultimate online security solution that many content creators claim. VPNs can help protect data in transit, obscure online activity from ISPs, and provide access to geo-restricted content. However, they are not designed to block malware, prevent ransomware, or shield users from phishing attacks. To maintain comprehensive online security, users must practice a range of protective measures beyond VPN use.
In today’s digital age, where content creators influence public perception, it’s essential for users to remain skeptical of advertisements that promise unrealistic security benefits. The responsibility for true online safety lies in awareness, cautious online behavior, and the use of a broader array of security tools and practices beyond a VPN.



